controlling thrips
 Adults are small, yellowish and have hair-fringed wings that are usually held across the back. Immature thrips are similar to adults but are wingless. Adult female thrips insert eggs into plant tissues. Just before hatching, the egg “squeezes” out of the tissue and hatches. Development progresses through two larval stages (instars), a pre-pupal non-feeding stage that crawls down into the soil, and a pupal resting stage from which adults emerge. Development from egg to adult takes 8 to 20 days depending on temperature.
Adults are small, yellowish and have hair-fringed wings that are usually held across the back. Immature thrips are similar to adults but are wingless. Adult female thrips insert eggs into plant tissues. Just before hatching, the egg “squeezes” out of the tissue and hatches. Development progresses through two larval stages (instars), a pre-pupal non-feeding stage that crawls down into the soil, and a pupal resting stage from which adults emerge. Development from egg to adult takes 8 to 20 days depending on temperature.
A great number of thrips are plant feeders. Both larvae and adults feed on flowers, leaves, twigs, or buds, using their piercing-sucking mouthparts, causing structural abnormalities of foliage in the form of leaf malformation (distorted, dwarfed, and matted), leaf fold, leaf roll, leaf blisters, and sometimes defoliation; causing discoloration of petals, deformation, or scarring of flowers.
When using insecticides, take steps to minimize exposure to bees and other insect pollinators when they are foraging on pollinator attractive plants around the application site.
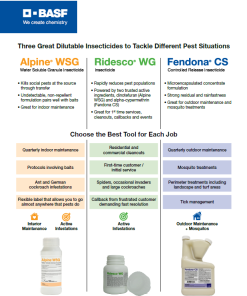
Insecticide Concentrates
– These concentrates are mixed with water and used in a compressed hand held sprayer to make your application.
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Cyzmic CS Micro encapsulated insecticide 8 oz. (Same as Demand CS)
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates
Spray Concentrates